Information presented on this web page is intended for informational and educational purposes only and is not meant to be taken as legal, financial, investment or tax advice. We do not accept any responsibility for any trading or investment related losses. Please review our disclaimer on before taking action based upon anything you read or see.
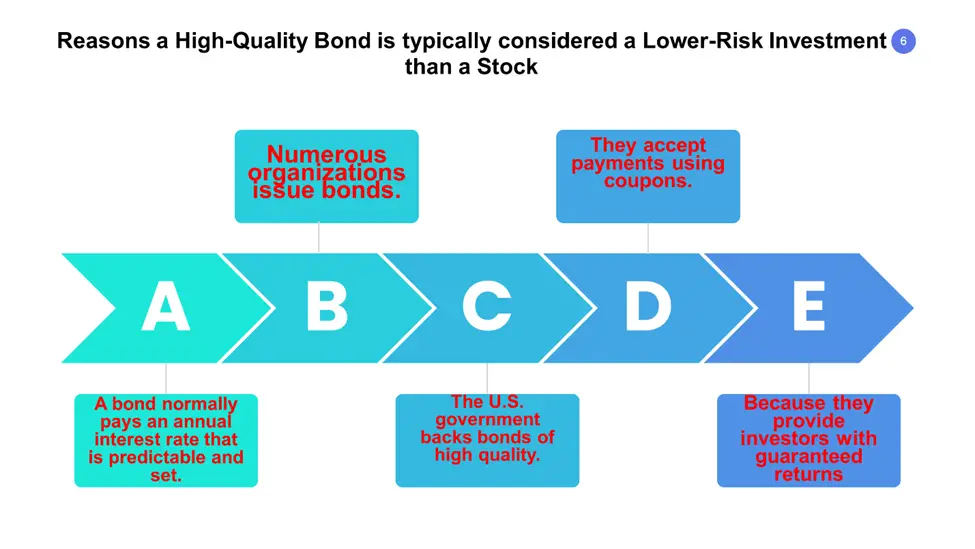
Long-term debt is represented via bonds. The bondholder promises to receive a set interest rate until the maturity date (typically twice a year) and the principal amount at maturity. Governments use bonds to fund government expenditures and businesses to support their expenses. These are the tools for growing a firm, implementing successful ventures, and refinancing corporate debt. So, why is a high-quality bond typically considered a lower-risk investment than a stock?
Because the issuer begins making payments within the first year, bonds are a short-term investment. Given the current inflation rate of 3%, the amount of interest rate distributions are usually modest, at 4% every year.
Bonds are considered a lower-risk investment since bond values are steadier than stock prices. Bondholders, like shareholders, can sell their bonds on the open market. The bond price is determined by subtracting the amount of interest that has already been paid to the bondholder.
According to seasoned investors, stocks and bonds should be evenly distributed in your investment portfolio. While young entrepreneurs are more likely to invest in long-term assets like stocks, investors planning for retirement believe bond investments to be more rewarding.
What is a High-Quality Bond?
Bonds with higher interest rates are considered high-quality since investment-grade bonds have better credit ratings. High-quality bonds must give investors a higher return than investment-grade bonds since they are more likely to fail.
High-quality bond issuers are often start-up businesses or capital-intensive organizations with high debt ratios. Some premium bonds, nevertheless, are fallen angels who have lost their stellar credit ratings.
A Short History of Bonds
Bonds were initially used in the 16th century to fund the various wars that were taking place at the time. By borrowing money from investors, governments could fund military operations without taxing citizens directly. Investors were compensated for their risk by receiving interest payments on their loans.
When governments began issuing new bonds to pay off their old ones, the process of “re-financing” their debt came to be known as “rolling over” existing bonds. This process of taking out new debt to pay off old debt is still used by governments today.
What is a Stock?
A stock is a kind of security that denotes ownership of a portion of the issuing business. Shares, also known as units of stock, entitle their owners to a share of the company’s assets and income in proportion to the number of shares they possess.
Most individual investors’ portfolios are built on stocks, which are mostly purchased and sold on trading platforms. Government standards that safeguard investors from dishonest tactics during stock trading must be followed.
Why are Bonds typically considered a lower-risk investment than stocks?
Bonds typically offer a lower rate of return than stocks, which means they are generally a lower-risk investment. The overall value of a stock is based on the predicted future value of the company: If analysts believe the company will experience rapid growth in the future, the company’s value will rise, and the stock will increase.
If analysts predict a company will experience a decrease in use, however, the value of the company will drop, and the stock value will fall. Investors who purchase bonds typically do not have to worry about a dramatic increase or decrease in the worth of the company behind the bond: They receive a predetermined interest rate over a specified time regardless of the health of the company that issued the bond.
Risk and Reward with Bonds
Bond investors are typically looking for a safe and steady return on their investment. Because bonds are considered a lower-risk investment than stocks, investors typically receive a lower interest rate on their bonds.
Investors also accept a lower interest rate in exchange for the certainty of receiving their expected payments. For example, if you purchase a corporate bond, the company may default on the loan and fail to pay you back. If you purchase a government bond, there is a slim chance that the government will default on the loan.
Most fixed-income bonds are issued with a set maturity date, after which the original loan is repaid in full. If the issuing company goes bankrupt before the maturity date, investors do not receive their interest payments as expected.
4 Primary Components of a Diversified Portfolio
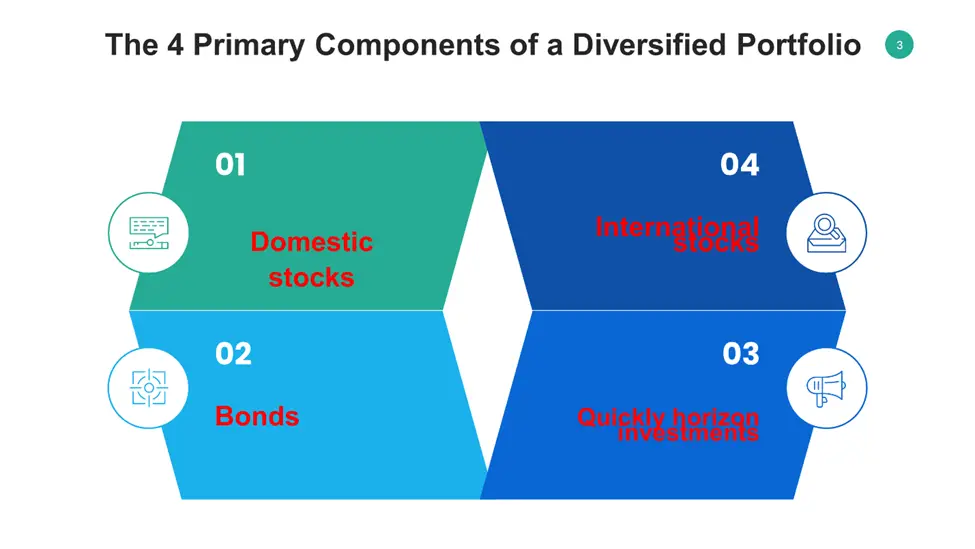
Domestic Stocks
The riskiest part of your portfolio, stocks, provide the potential for larger gain over the long term. However, a higher risk is associated with this increased development potential, especially in the near term. Your stock investment may lose value if and when you decide to sell it since equities are often more volatile than other investments.
Bonds
Most bonds pay out interest consistently and are seen to be less volatile than equities. They often perform differently than equities, which may provide a buffer against the unexpected ups and downs of the stock market. US Treasury or other high-quality bonds are often preferred by investors who are more concerned with safety than growth.
Since many bonds—especially slightly elevated issues—generally don’t give returns as high as stocks over the long run, these investors may have to settle for lower long-term returns. Though they come with more risk, certain fixed income assets, such as high-yield bonds and some overseas bonds, may provide much higher rates.
Quickly horizon investments
These include short-term certificates of deposit and money-market funds. Money-market funds are cautious investments that provide stability and simple money management. They are perfect for those who want to keep their principle. Money market funds often provide lower returns than bond funds or individual bonds in exchange for that degree of safety.
Unlike many CDs, money market funds are not insured or backed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), even though they are considered safer and more conservative. However, you risk giving up the liquidity that money market funds often provide when you invest in CDs.
International stocks
The performance of stocks issued by non-US corporations often differs from that of their US equivalents. This exposes you to possibilities that US securities do not provide. Consider including foreign equities in your portfolio if you’re looking for assets with both larger potential rewards and higher risk.
Additional Components of a Diversified Portfolio
Investing will always come with some level of risk. You can’t avoid this risk as an investor, no matter how educated you are (if the financial crisis taught us anything, it’s that even pros don’t always make the correct decisions regarding the market).
With this in mind, it’s critical to be realistic about the returns you may anticipate from a well-diversified portfolio. It’s reasonable to expect lower risk and more consistent returns, yet, it’s unrealistic to expect your portfolio to remain unaffected if the macroeconomic environment changes drastically.
Diversification is a risk-management strategy in which investors spread their risk over various asset classes, financial instruments, sectors, and other categories. Diversification’s fundamental purpose is to reduce the impact of volatility on a portfolio, not to enhance profits.
According to most investing professionals, diversification is the most critical component of an investment plan that accomplishes long-term financial goals while limiting risk.
Bond vs Stock
The distinctions between bonds and stocks have been highlighted in the table below.
| Bond | Stock |
| Bonds are loans you make to businesses or the government. | Stocks signify a company’s equity or portion of ownership. |
| In the near term, U.S. Treasury bonds are often more stable than equities, although, as was said above, this reduced risk usually results in lower returns. | The value of your shares declining after you buy them is the largest risk associated with stock transactions. |
| Depending on the bond’s terms, the holders of such bonds have a far higher priority. | In the case of a company’s liquidation, its stockholders have the last claim to any remaining funds. |
| Bondholders are not allowed to vote. | Stockholders have the right to cast ballots on some corporate matters, such as the election of directors. |
| Bonds often signify debt. | Simply put, stocks are ownership shares in businesses. |
| Bonds have poor returns, and their interest rates may only rise as fast as inflation. | Stocks often increase along with the economy and may aid in avoiding inflation. |
Importance of Quality When Investing in Bonds
The overall risk of default associated with a given bond is referred to as its quality. The bond’s credit rating typically measures quality: The higher a bond’s credit rating, the lower its risk of default.
Most governments issue bonds with a “AAA” credit rating, which represents the least amount of risk you can take when investing in a bond. Investors can also purchase bonds issued by companies considered “investment grade” – or likely to be able to repay the loan.
Best Low-Risk Investments in 2022
The stock market made a significant comeback in the second part of last year and has remained hot since then. However, if the market cools, investors should maintain their discipline. Building a portfolio with at least some lower-risk items will help weather future market turbulence.
The trade-off, of course, is that investors are more likely to receive lower long-term profits by reducing risk. If you aim to protect cash and provide a consistent stream of interest income, it may be suitable. So, we can consider these low-risk investments:
Savings accounts with a high rate of return
Savings accounts, though not strictly an investment, provide a modest return on your money. You can locate the highest-yielding alternatives by searching online, and if you’re prepared to look at the rate tables and shop about, you can obtain a bit more yield.
In the sense that you will never lose money in a savings account, it is safe. The government guarantees most funds up to $250,000 per account type per bank, so you will be paid even if the financial institution fails.
Bonds of savings
Savings bonds provide a low to no risk, but they may also offer a low or no return.
Consequently, over time, your currency value is likely to dwindle. If acquired after May 2005, Series EE bond funds pay the interest lasting up to 30 years and have a fixed rate of return. A fine equal to the last three months’ dividend is imposed if a US investment bond is cashed before five years.
Deposit certificates
In an FDIC-backed account, bank CDs always are loss-proof until you collect the cash out early. To get the best rates, research online and evaluate what institutions offer. The bank commits to paying you a predetermined interest rate if you hold the CD until the end of the period. Some term deposits provide higher interest than CDs. However, these “high-yield” accounts may need a large deposit.
Money market funds are a type of mutual fund.
Investment funds are risk-spreading pools of CDs, short treasuries, and low-risk securities that brokerages and mutual fund providers sell. Unlike a CD, a bond fund is fluid, implying you may take your funds immediately without penalty. Term deposit funds are generally considered to be safe investments.
Treasury bills, notes, bonds, and TIPS are all examples of government debt.
These securities are very liquid and may be purchased and sold directly or through mutual funds.
Unless you acquire a negative-yielding bond, you will not lose money if you hold Treasury until they mature. If you sell them before they grow, you risk losing some of your principles since the value fluctuates with interest rates. However, some Treasury may have a negative yield due to recent market volatility and the Federal Reserve’s decision to cut interest rates to zero.
Bonds issued by corporations
Corporations can also issue bonds, ranging from low-risk (issued by large profitable enterprises) to high-risk (issued by smaller, less successful companies). High-yield bonds, sometimes known as “junk bonds,” are the lowest of the low. Although neither asset type is risk-free, adhesives are typically believed to be less risky than stocks.
Stocks that pay dividends
Dividend-paying stocks are regarded to be less risky than non-dividend-paying equities. Stocks are not as secure as cash, bank deposits, or treasury securities, although they are more secure than elevated assets such as futures and options.
Dividend companies are safer than high-growth equities since they provide cash dividends, reducing but not eliminating volatility. As a result, dividend stocks will vary with the market, but they may not fall as much when it is down.
Stocks with a higher dividend yield
Preferred stock, like a bond, pays a monthly cash dividend. On the other hand, companies that issue preferred stock may be entitled to suspend the dividend in particular situations, albeit they must usually make up any missing payments. In addition, before you may pay dividends to common stockholders, the corporation must pay preferred stock distributions.
Accounts in the money market
A money market account resembles a savings account and features many of the same features, such as a debit card and interest payments. On the other hand, a money market account may have a more significant minimum deposit than a savings account. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insures money market accounts up to $250,000 per depositor per bank.
As a result, money market accounts do not put your money at risk. The penalty of having too much money in your account and not generating enough interest to keep up with inflation is perhaps the most significant danger since you may lose purchasing power over time.
Annuities with a set rate of return
An annuity is a contract, usually negotiated with an insurance company that promises to pay a set amount of money over a set period in return for a lump-sum payment. The annuity can be structured in various ways, such as spending over a certain amount of time, such as 20 years, or until the client’s death.
A fixed annuity is a contract that promises to pay a set amount of money over a certain period, generally monthly. You can contribute a lump sum and start receiving payments immediately, or you may pay into it over time and have the annuity start paying out later (such as your retirement date.)
Additional components of a diversified portfolio
Investing will always come with some level of risk. You can’t avoid this risk as an investor, no matter how educated you are (if the financial crisis taught us anything, it’s that even pros don’t always make the correct decisions regarding the market).
With this in mind, it’s critical to be realistic about the returns you may anticipate from a well-diversified portfolio. It’s reasonable to expect lower risk and more consistent returns, yet, it’s unrealistic to expect your portfolio to remain unaffected if the macroeconomic environment changes drastically.
Diversification is a risk-management strategy in which investors spread their risk over various asset classes, financial instruments, sectors, and other categories. Diversification’s fundamental purpose is to reduce the impact of volatility on a portfolio, not to enhance profits.
According to most investing professionals, diversification is the most critical component of an investment plan that accomplishes long-term financial goals while limiting risk.
Factoring time into your Diversification Strategy

Factor investing is selecting assets based on characteristics linked to greater returns. Macroeconomic and style factors are the two primary variables influencing stock, bond, and other asset returns. The former seeks to explain returns and hazards within asset classes, whereas the latter tries to capture broad risks across asset classes.
The inflation rate, GDP growth, and unemployment rate are all standard macroeconomic parameters. The corporation’s creditworthiness, share liquidity, and stock price volatility are all microeconomic elements. Growth vs value stocks, market capitalization, and the industrial sector are all style considerations.
The Equity Risk Premium
It’s the gap between the stock market’s projected returns and risk-free assets’ expected returns. It would help if you made a few assumptions to compute risk premiums. So, it’s possible that the equity risk premium isn’t a suitable signal for deciding whether to purchase stocks or bonds.
The US Federal Reserve looked at 20 different methods for calculating the equity risk premium and found that the results differed drastically. Finally, people who utilize the equity risk premium must use it as a guide rather than mathematical certainty.
The phrase “equity risk premium” refers to the extra return from investing in the stock market above a rate risk. This additional return compensates investors for the additional risk associated with equities investing. The magnitude of the premium fluctuates and is determined by the risk level in a particular portfolio. It also swings over time as market risk changes.
The risk-reward trade-off is the basis for an equity risk premium. The premium is theoretical because it is a forward-looking value. However, no one can predict how much money an investor will make since no one can predict how healthy shares or the equity market will do in the future.
How to Compare the Risk of Bonds and Stocks
According to financial theory, assets with more risk should have higher anticipated returns. Bonds are less risky than stocks since stocks are often more volatile. As a result, investors anticipate higher average returns from stocks, which has long been the case.
However, the likelihood of losing money increases with risk. Stock investors need to be more risk-averse and prepared to sometimes take big losses. A greater portion of an investor’s cash may be better spent on investment-grade corporate or U.S. Treasury bonds if they are risk-averse or want more investment stability. The many risk categories connected to bonds and equities are broken out here.
Investment-grade corporations or U.S. Treasury bonds are also typically thought to bear almost no default risk but might sometimes undergo negative price swings in the intermediate term owing to rising interest rates. However, as mentioned above, reduced risk generally entails lower returns.
Pros & Cons of investing in Bond vs Stock
The Pros & Cons of investing in Bond vs Stock have been highlighted in the table below.
| Bond | Stock |
| Bonds are seen to be a more secure investment than equities. Corporate bonds, as opposed to equities, are less likely to lose all of their value if you invest in them. | Stock returns historically have been among the greatest. |
| Bonds are simple to acquire and may be exchanged on secondary markets before maturity. | Within brokerage accounts and other trading platforms, trading stocks is simple. |
| Because bonds are transferable, they make wonderful presents for younger relatives and friends. | Investors often consider the many stocks or funds accessible to them in large quantities of information. |
| Most bonds come in a variety of terms. | The riskiest stock investments also provide the largest returns. Wealth may be destroyed fast by a market slump. |
| When you buy bonds, you give up potential in favour of security. Bonds do carry some risk. When faced with challenges, the issuing corporation may find it difficult to keep its repayment commitments. | Stock market manipulation attempts are more common than ever. The value of stocks might fluctuate greatly. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Bonds are typically more stable and risky than stocks, but they can also deliver consistent returns that are steady and unyielding. The attraction for investors is that bonds offer a low-risk Rating Dilemma, which is attractive to banks and other investors. Interest rates on bonds frequently tend to be greater than savings rates at banks, CDs, or money market accounts.
Someone with more to lose or less willing to take a risk may choose a low-risk investment. They provide stability and security, but because the risk is lower, the return is smaller in principle and typically ranges from 1 to 5% yearly. As a result, this is a method of generating a steady income or preserving wealth.
These include cash or government bonds and money market bonds because savings accounts are less hazardous than equities or shares.
This is also a fantastic option for those who want funds rapidly. For example, if you have $20,000 and need to deposit a house next year, you will most likely pick low-risk investments.
If the $20,000 is going towards a beach property in the far future, however, a high-risk investment may be preferable because you will have more time to recover any losses. It’s also less likely that you’ll be compelled to sell out of position too soon.
Savings account in the form of investment that generally bears the least risk. CDs, bonds, and money market accounts are among the safest investment options. Because these financial products have a low market exposure, they are less influenced by market volatility than stocks or mutual funds.
The bigger the investment’s potential return, the bigger the risk. No assurance that taking on greater risk will result in a more significant return. Diversification allows you to lower your portfolio’s risk while preserving possible profits.
A money market account is typically more attractive than conventional savings account in return for more significant balance requirements; some provide check-writing privileges and ATM access. Certificate of deposit: typically has the highest interest rate among savings accounts and the most restrictive access to money.
Generally, expanding into bonds may offer a buffer that protects shareholders from the full effect of a sharemarket slump. However, it’s important to remember that some bond market instruments, such as bond ETFs are likely to lose money when equities fall.
Bonds are generally safe investments, but they have their own hazards. Unlike stocks, which are exchanged on exchanges, bonds are traded over the counter. You’ll have to acquire them through a broker, especially if you’re buying corporate bonds. Remember that depending on the broker you pick, you may have to pay a premium.
Bonds have several disadvantages, including interest rate rises, price fluctuations, and counterparty risk. When interest rates fall, bond prices rise, and when interest rates rise, bond prices fall. Your bond fund may suffer market rate deficits in a growing rate environment.
Compared to a regular bank savings or checking account, online savings and cash management accounts provide better rates of return. Cash management accounts are a cross between protection and a checking account: They may pay similar interest rates as savings accounts, but they are usually offered by brokerage firms and may include debit cards or checks.
If you have savings accounts, try them out. They’re excellent for short-term savings or money you only need to access once in a while, like an emergency or vacation fund. A savings account can only make six transactions each month. Cash management accounts provide more flexibility and, in some situations, more excellent interest rates than traditional savings accounts.
Higher risk is linked to a higher chance of a higher return, whereas lower risk is connected to a higher event of a lower return. The risk-return trade-off is an investor’s trade-off between risk and profit while making investment decisions.
For a long time, the stock market has been regarded as the source of the highest historical returns. A higher level of risk accompanies higher rewards. The price of a stock is more variable than the price of a bond. Stocks are less trustworthy over shorter periods.
Bottom Line
While it is impossible to invest directly in a “risk factor,” a risk-based allocation approach can assist investors in selecting a mix of asset classes that best diversifies their risks while expressing their views on the global economy and financial markets. What would be the effects of such a strategy? Investors may pick which asset class allows them to acquire exposure to a specific risk factor most efficiently by understanding the underlying risk factors inside multiple high-quality bonds classes.
Expert Opinion
Selecting investments is one of your most crucial choices while creating your portfolio. Even though there are dozens of investing possibilities, stocks and bonds should make up most of your portfolio. These two forms of investments fundamentally differ regarding risk exposure and response to changing financial conditions.
You can make better judgments and build a portfolio that suits your requirements if you know each investment’s benefits and drawbacks. At this point, the above tips will aid you immensely.
Resources
- https://gocardless.com/guides/posts/what-is-portfolio-diversification/
- https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/investing/stocks-vs-bonds
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/09/difference-between-bond-stock-market.asp
- https://www.accountingtools.com/articles/what-is-the-difference-between-stocks-and-bonds.html
- https://www.thebalance.com/the-difference-between-stocks-and-bonds-417069
- https://www.northwesternmutual.com/life-and-money/whats-the-difference-between-stocks-and-bonds/





